THE PITFALLS OF 'MORE, YOUNGER' MINDSET Why Starting Kids Too Early and Pushing Them Too Hard Can Backfire in Youth Sports
Better Coaching
DECEMBER 24, 2024
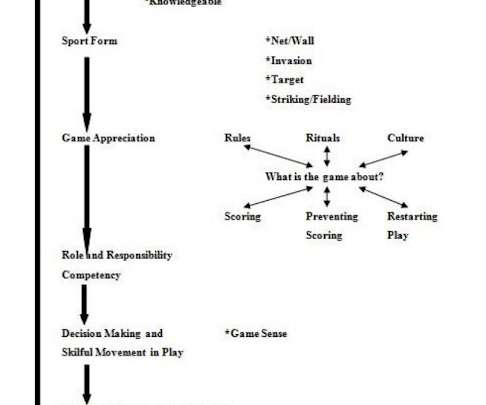
More, Younger Youth sports occupy a special place in American culture, shaping childrens character, health, and social lives. Across the United States, an increasing number of parents and coachesoften with good intentionsseek to introduce sports to children at younger and younger ages and with greater intensity than ever before.
























Let's personalize your content