The Relentless School Nurse: Embracing “Exercise Snacks” For a Healthier You!
Relentless School Nurse
SEPTEMBER 14, 2023
When you hear “exercise snacks,” you might think of a protein bar or a piece of fruit. In 2023, consider incorporating these short bursts of activity into your daily routine to help achieve the recommended 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week.



























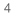

Let's personalize your content